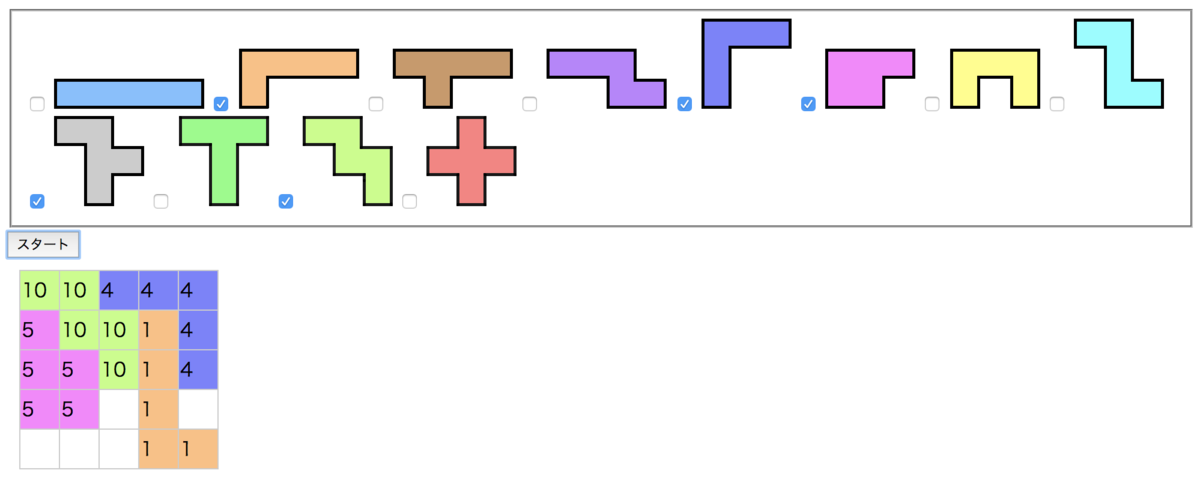
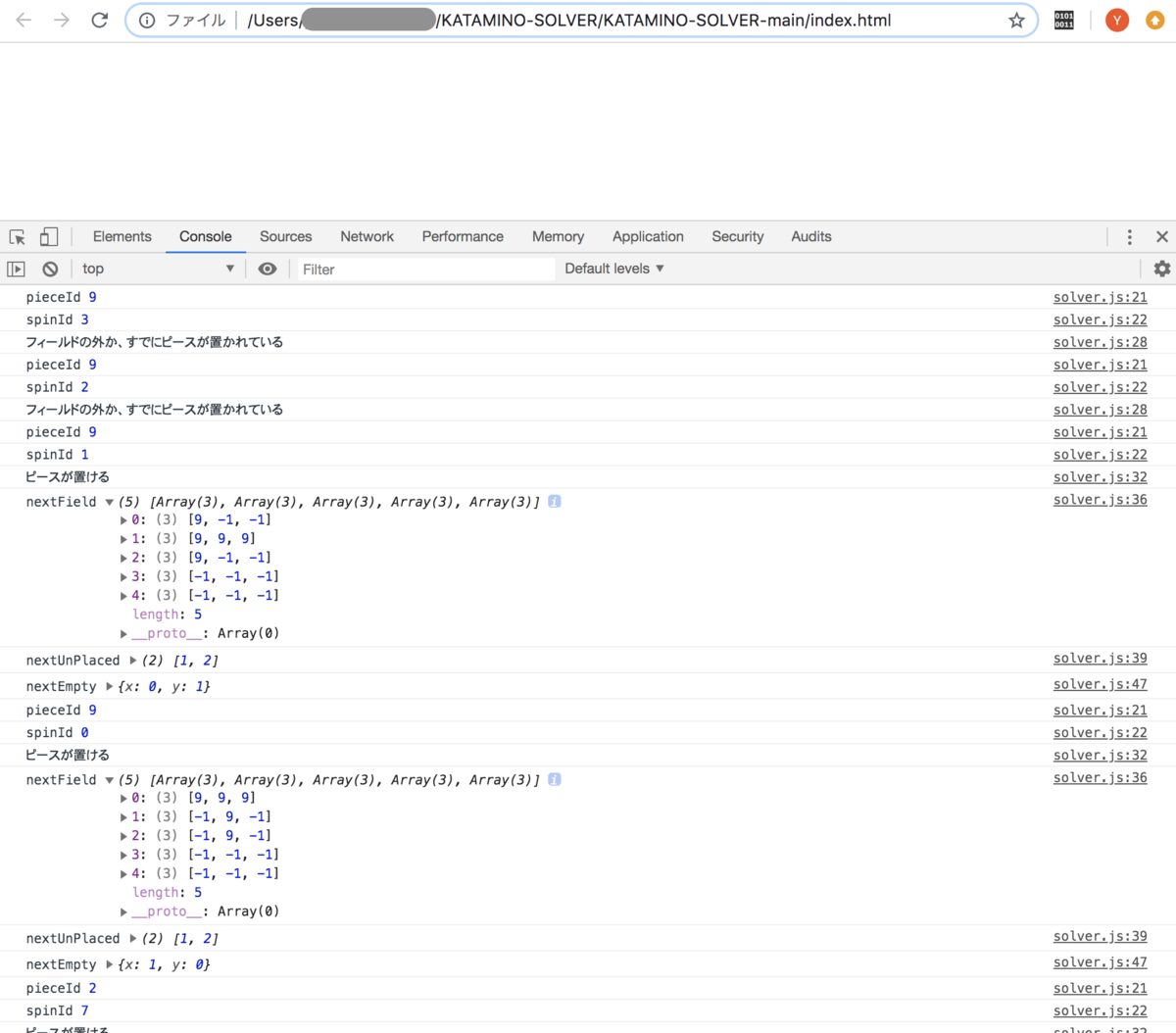
★前回の記事
前回まででピースを画面から選ぶことができ、解く過程も表示することができました。 いくつかの組み合わせを試してみると、以下の画像のように、フィールドに穴が空いている場合でも、ピースを置くのを続けてしまう場合があることに気づきます。
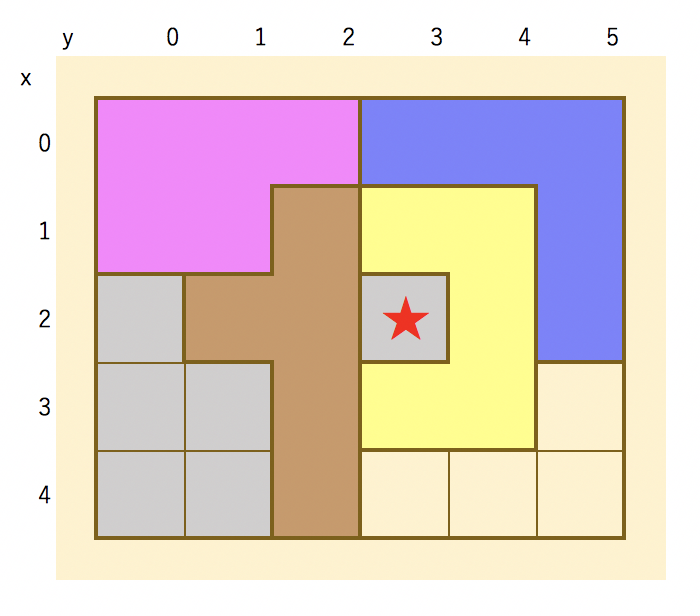
★印のような穴が空いてしまっても、解くのを続けてしまう↓
今回は、穴が空いてしまった場合に処理を中断する処理を入れます。
実装方針
穴が空いてしまっている状況は、フィールドが分断されている状態です。分断を検知するアルゴリズムはいくつかありますが、今回は上下左右に連続したマスを数えることで分断を検知します。 ただし、分断されていても問題ないケースがあります。それは分断された個々のフィールドにピースが置ける場合です。
穴が空いてしまってこれ以上置けない例↓
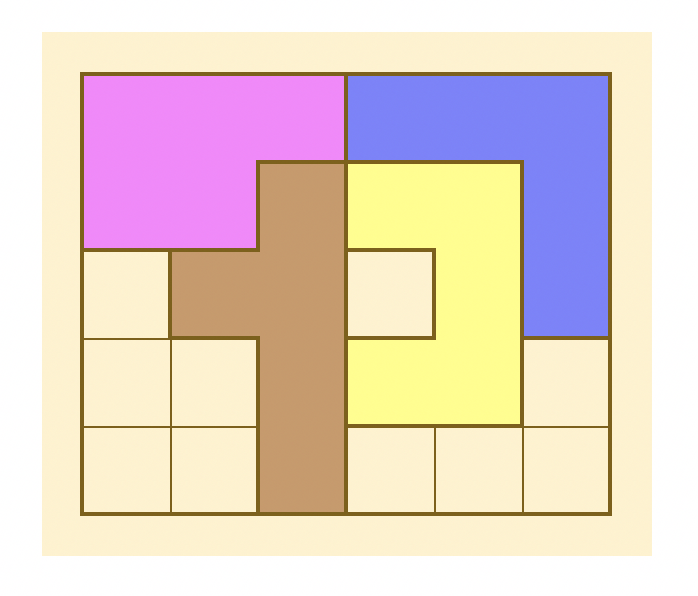
フィールドは分断されているがまだピースが置ける可能性がある例↓

これら2つの例の違いは、個々の分断されたフィールドのマスの個数が5の倍数かどうかです。 KATAMINOのピースは5個の正方形をつなげてできる形なので、5の倍数の連続したマスであれば、ピースが置ける可能性があるのです。
そこで、連続しているマスの個数を数え、それが5の倍数であるかどうか判定します。5の倍数であればそのまま解くのを続け、そうでなければこれ以上スタックにデータを投入しないようにします。
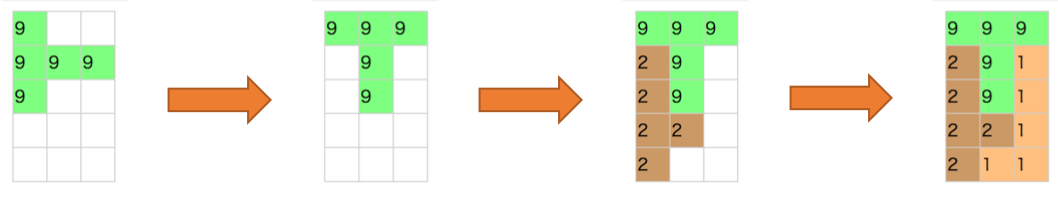
連続するマスの数を求めるアルゴリズムを考えましょう。探索のアルゴリズムが使えそうです。 起点となる空白マスから、上下左右に空白マスを探します。空白マスを見つけたら空白マスの個数をカウントアップし、マスを訪問済みにマークします。 今回は幅優先探索で実装してみましょう。キュー(queue)を使用します。アルゴリズムは以下のようになります。
- 起点となる空白マスをキューに入れる、空白の個数を0に初期化する
- キューから1つ、マスのデータを取り出す
- マスが空白でない、または訪問済みであったら1に戻る
- マスが空白だったら、カウントを1つ増やし、マスを訪問済みにする
- 上下左右のマスをキューに入れる
- 2に戻る
これを繰り返した図が以下となります。
{x:2, y:0}(★マークのマス)を起点とする場合。{x:2, y:0}を訪問済みにマークする(図では灰色の背景で表現)↓

上下左右のマスをキューに投入する(フィールドの範囲外でも気にせず投入する)↓

キューから先頭(図では一番左)の要素({x:3, y:0})を取り出し、訪問済みでない空白なので、訪問済みにマークする。↓

上下左右のマスをキューに投入する(フィールドの範囲外でも気にせず投入する)↓

キューから先頭(図では一番左)の要素({x:2, y:1})を取り出す。空白マスでないので、次のデータをキューから取り出す↓

以下、繰り返す
実装
はじめに、スタブを作成し、呼び出し側の実装をします。
js/solver.js
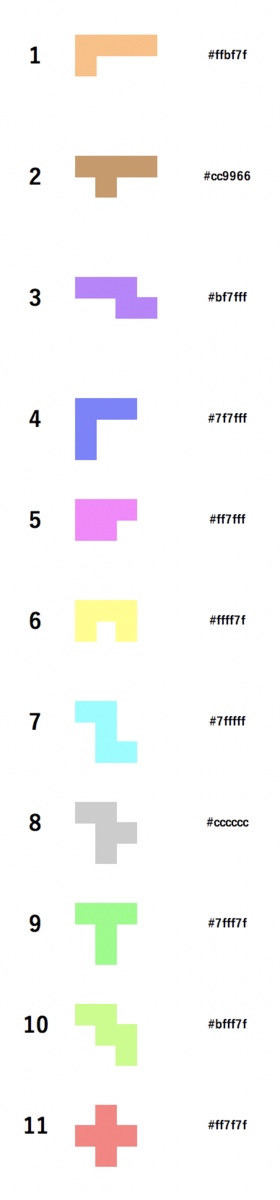
const solver = { // 中略 solve : () => { if (solver.solverStack.length <= 0) { console.log("解けなかった") return } const {kataminoField, minEmpty, pieceId, spinId, spin, unPlacedPiece} = solver.solverStack.pop() // 中略 display.show(nextField) if (nextUnPlaced.length <= 0) { console.log("完成") return } const nextEmpty = solver.findNextEmpty(nextField, minEmpty) console.log("nextEmpty", nextEmpty) // 追加ここから if (! solver.hasAllFiveTimesCells(nextField, nextEmpty)){ console.log("フィールドが5の倍数以外で分断されている") setTimeout(solver.solve, 300) return } // 追加ここまで nextUnPlaced.forEach((nextPieceId) => { KATAMINO_ARR[nextPieceId].forEach((nextSpin, nextSpinId) => { solver.solverStack.push({kataminoField: nextField, minEmpty: nextEmpty, pieceId:nextPieceId, spinId:nextSpinId, spin: nextSpin, unPlacedPiece: nextUnPlaced,}) }) }) setTimeout(solver.solve, 300) }, // 中略 // 追加ここから /** * 全ての連続した空白マスの数が5の倍数か判定します */ hasAllFiveTimesCells: (kataminoField, minEmpty) => { // TODO 実装 return false }, /** * emptyPlaceを含む連続した空白マスの個数が5の倍数か判定します */ hasFiveTimesCells: (kataminoField, emptyPlace) => { // TODO 実装 return false }, // 追加ここまで }
hasAllFiveTimesCellsは全ての連続した空白マスの数が5の倍数か、hasFiveTimesCellsはemptyPlaceを含むフィールドが5の倍数のマスを持つかを判定します。hasFiveTimesCellsの中で、見つけた空白のセルを訪問済みにマークします。
hasAllFiveTimesCellsを実装します。この関数の中では、1つの空白マスをhasFiveTimesCellsに渡し、その空白マスから連続した空白マスを訪問済みにマークしてもらいます。その後、まだピースが置かれていない、かつ訪問済みでない空白マスを見つけ、上記を繰り返します。訪問済みでない空白マスがなくなったとき、全て5の倍数の連続した空白マスであれば、trueを返します。
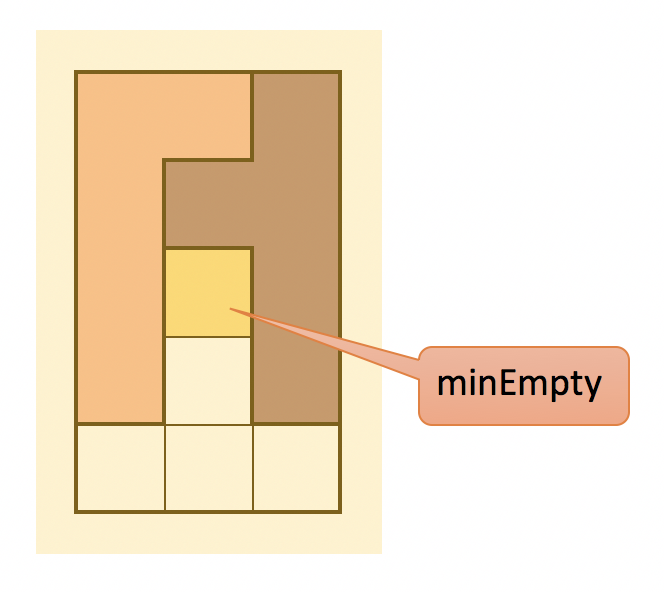
minEmpty(★印のマス)↓

minEmpty(★印のマス)を含む連続した空白マスを訪問済みに訪問済みにマーク(図では灰色の背景で表現)↓
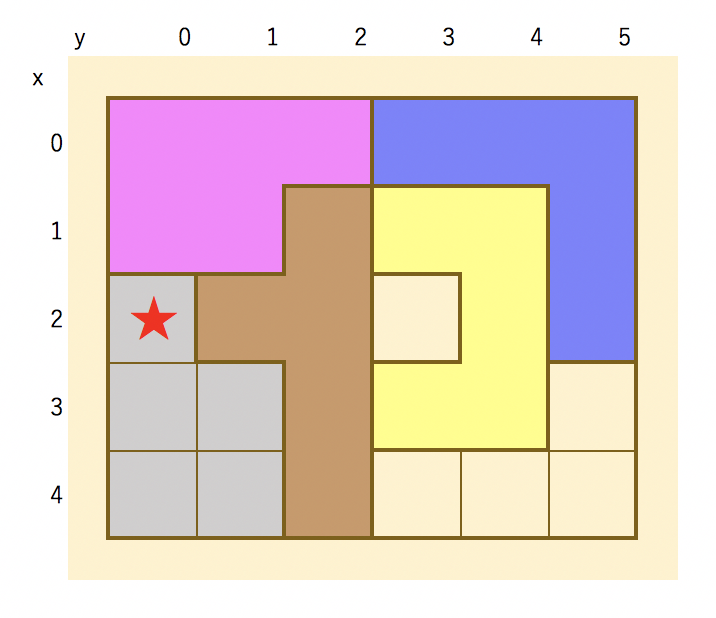
次の訪問済みでない空白↓

★印のマスを含む連続した空白マスを訪問済みに訪問済みにマーク↓
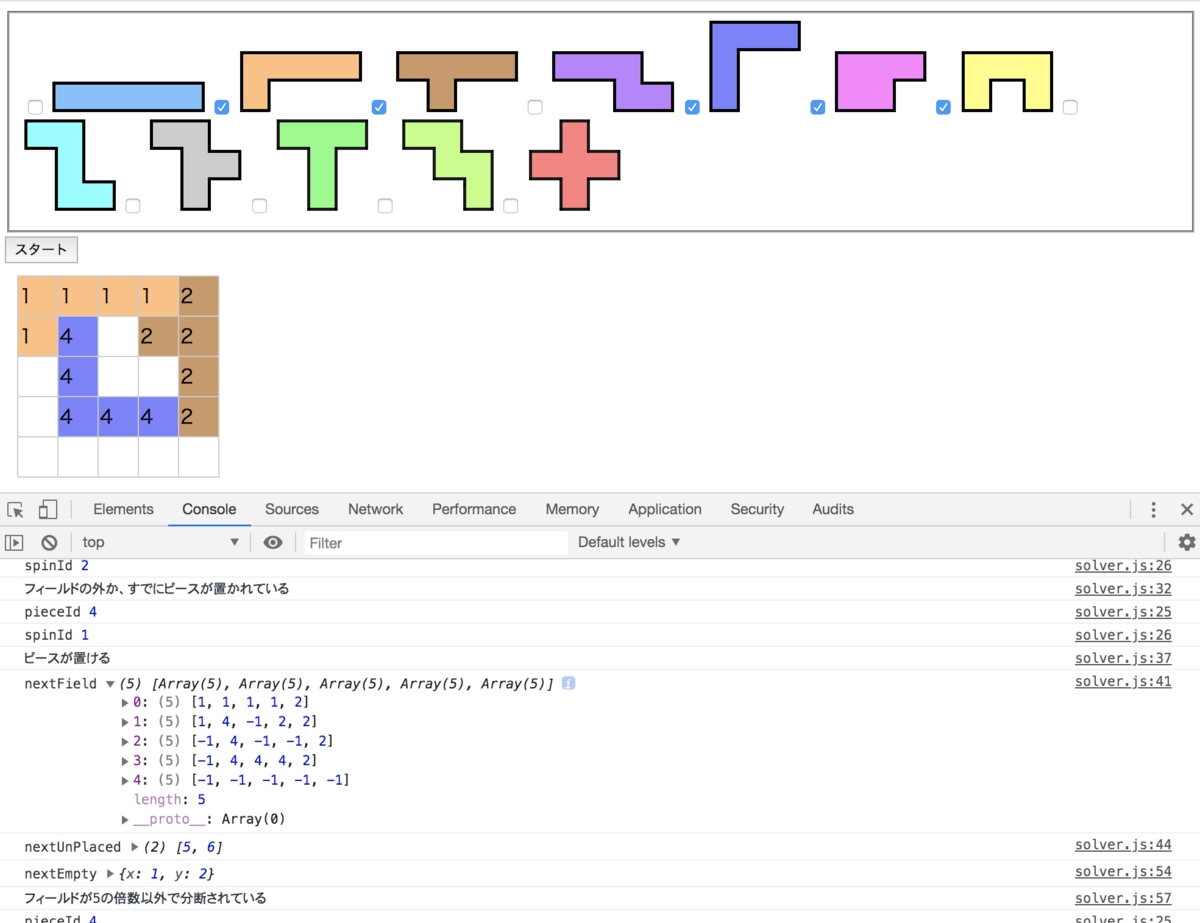
hasFiveTimesCellsの中で、フィールドの内容を更新するので、引数に受け取ったkataminoFieldをコピーします。2次元配列なので、util.copyArrayOfArrayを使用します。
hasFiveTimesCellsに渡す空白マス(nextEmpty)は、minEmptyで初期化します。
nextEmptyが存在する場合は、hasFiveTimesCellsを呼び出します。
次の空白の更新にはfindNextEmpty関数を使用します。
js/solver.js
hasAllFiveTimesCells: (kataminoField, minEmpty) => { const kataminoFieldCopy = util.copyArrayOfArray(kataminoField) let nextEmpty = minEmpty while (nextEmpty) { if (! solver.hasFiveTimesCells(kataminoFieldCopy, nextEmpty)) { return false } nextEmpty = solver.findNextEmpty(kataminoFieldCopy, nextEmpty) } return true },
現在の実装では、空白がなくなったときにfindNextEmptyを呼び出すと配列の範囲外の値を返すので修正します。空白がなくなったときにundefinedを返します。
js/solver.js
findNextEmpty : (kataminoField, previousEmpty) => { // 変更ここから const minEmptyX = kataminoField.slice(previousEmpty.x).findIndex(row => row.some((val) => val < 0) ) if (minEmptyX < 0) { // 空白マスが見つからなかった return undefined } const x = previousEmpty.x + minEmptyX // 変更ここまで const y = kataminoField[x].findIndex(val => val < 0) return {x, y} },
hasFiveTimesCellsを実装します。emptyPlaceでキューを初期化します。
キューにデータがあるあいだ、キューからデータを取り出し、取り出した部分が空白であればカウントアップし、セルの値を100(適当な正の値)に更新します。その後上下左右のマスをキューに投入します。
最後に連続した空白マスの数が5の倍数かを返します。
js/solver.js
hasFiveTimesCells: (kataminoField, emptyPlace) => { const queue = [emptyPlace] let count = 0 while (queue.length > 0) { const currentPlace = queue.shift() if (! solver.isEmpty(kataminoField, currentPlace)) { continue } count++ kataminoField[currentPlace.x][currentPlace.y] = 100 queue.push({x:currentPlace.x + 1, y: currentPlace.y}) queue.push({x:currentPlace.x, y: currentPlace.y + 1}) queue.push({x:currentPlace.x - 1, y: currentPlace.y}) queue.push({x:currentPlace.x, y: currentPlace.y - 1}) } return count%5 === 0 },
動作確認
実行結果です。フィールドが分断された時に処理を中断しているのが分かります。
画面の表示でも、無駄にピースを置く回数が減っているのが分かります。
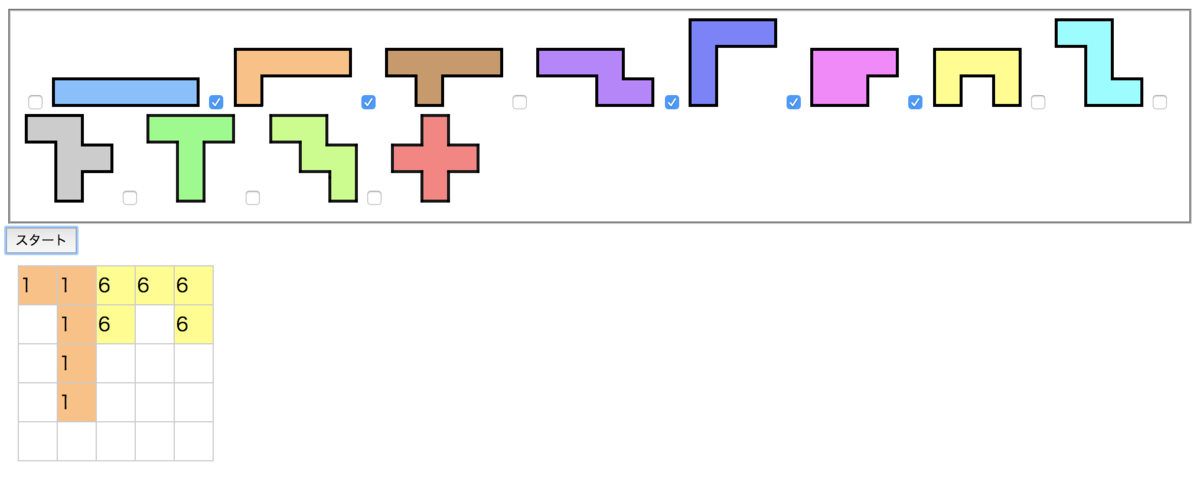
以上でフィールドが分割された時に探索をやめることができました。
KATAMINOを解くアルゴリズムのSTEP1は以上になります。この連載ではこれ以上アルゴリズムの改良はしませんが、まだまだ改良の余地があるので、ご自身でチャレンジしてみてください。
★次回の記事
★目次
![[商品価格に関しましては、リンクが作成された時点と現時点で情報が変更されている場合がございます。] [商品価格に関しましては、リンクが作成された時点と現時点で情報が変更されている場合がございます。]](https://hbb.afl.rakuten.co.jp/hgb/182e4377.af19d097.182e4378.b6c07045/?me_id=1227356&item_id=10000912&m=https%3A%2F%2Fthumbnail.image.rakuten.co.jp%2F%400_mall%2Fnewton-style%2Fcabinet%2Fretail_img%2Fns%2Fkom259200.jpg%3F_ex%3D80x80&pc=https%3A%2F%2Fthumbnail.image.rakuten.co.jp%2F%400_mall%2Fnewton-style%2Fcabinet%2Fretail_img%2Fns%2Fkom259200.jpg%3F_ex%3D240x240&s=240x240&t=picttext)